Choosing the right payment method is crucial when exporting, as it sets the terms for when and how you will receive payment from your buyer. This decision is more complex than for domestic sales due to various international factors.
A payment method is an agreement between you and your buyer that outlines the terms for payment. It’s essential to consider:
- Your buyer’s preference
- Market requirements
- Your financial situation
New exporters often request up-front payment to reduce risks and manage cash flow. However, some markets, such as large US-based retail chains, demand credit terms, which you often must comply with to become a vendor.
Common Export Payment Methods
Each payment method carries risks for both the seller (exporter) and the buyer (importer). Choosing the right method involves balancing these risks and finding an agreement that works for both parties.
Here are some common methods:
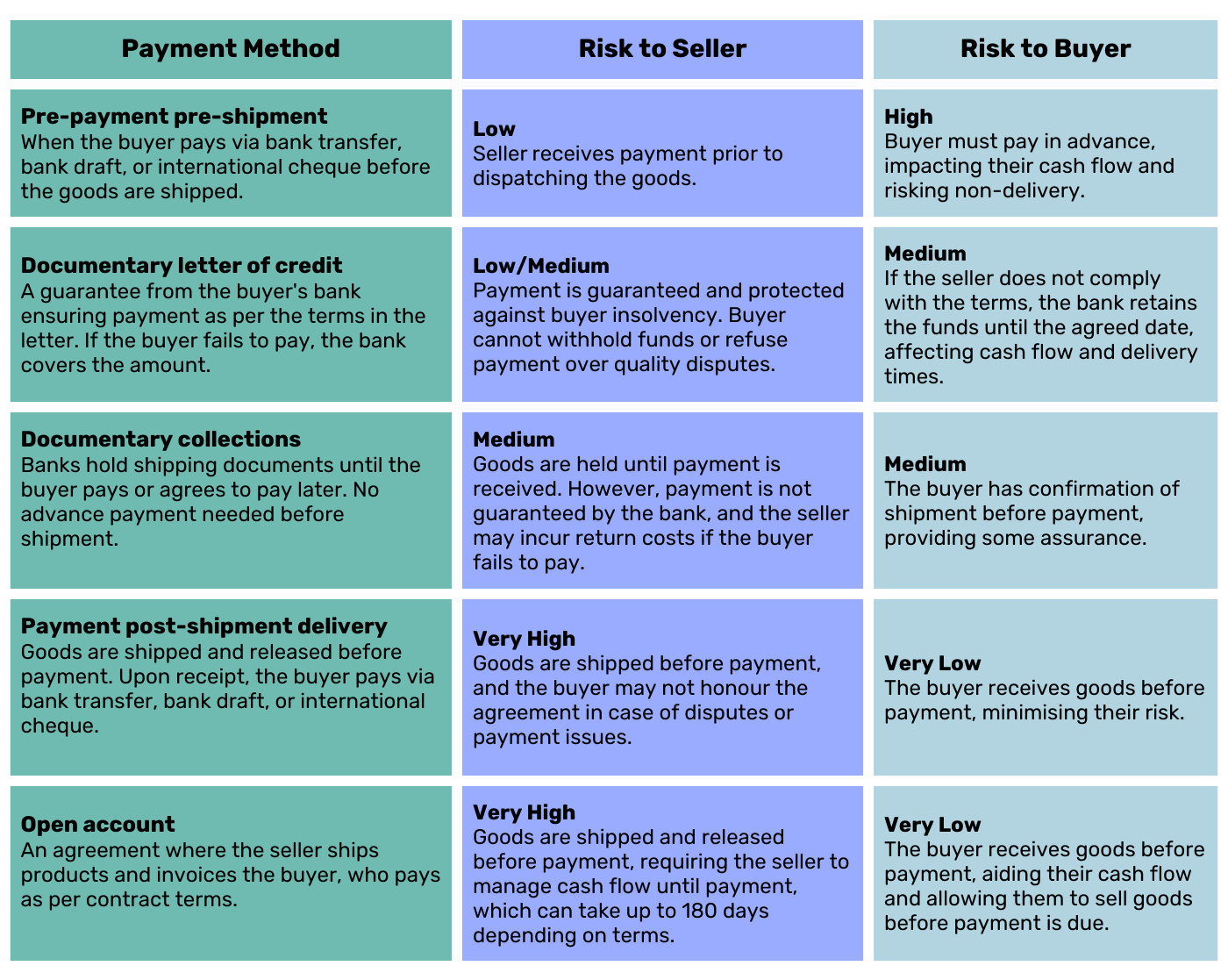
Managing Payment Risks
Payment risks in international trade include the possibility of late or non-payment by the buyer and variations in currency exchange rates. These risks can significantly impact cash flow and may result in lost income or profits.
To mitigate these risks, businesses can utilise trade loans or shipping guarantees and should always consider potential currency exchange fluctuations.
Trade Loans
A trade loan or trade finance loan is a short-term working capital loan designed to assist in financing trade commitments. You can apply for a trade loan at any stage of the export or trade transaction, depending on your needs at that time.
Situations for Trade Loans:
- Awaiting Payment from a Buyer: When there’s a delay in receiving payment.
- Buyer Default or Insolvency: If a buyer defaults on payment or becomes insolvent.
- Financing Shipment: Under documentary collections, post-shipment payments, or open account terms.
- Supporting Increased Production: To manage an increase in production volumes of your product.
Trade loans are usually provided as an advance of funds in either domestic or foreign currency. If traditional banks can’t assist, Export Finance Australia might offer the needed support.
Shipping Guarantees
Shipping guarantees fall under a letter of credit with a full set of documents of title to the goods. Banks issue shipping guarantees to the buyer’s customs broker or freight forwarder, allowing the release of goods that have arrived ahead of the shipping documents.
Benefits of Shipping Guarantees:
- Guaranteed Payment: When the buyer receives the goods.
- Protection Against Non-payment: Coverage if the buyer refuses to pay or becomes insolvent.
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations
When dealing with foreign currencies, managing fluctuations in currency exchange rates is crucial.
Options to manage exchange rate fluctuations include:
- Foreign Exchange Market (Forex): Allows conversion of one currency to another. You can invoice in the customer’s local currency and convert to AUD when the rate is favourable.
- Foreign Exchange Hedge: Arranged by your bank, a fixed exchange rate agreement helps avoid market fluctuations. The amount invoiced is the amount received.
